There are many underlying causes of a stiff back and knowing the short list of possible causes of your back stiffness will help you have a more productive discussion with your doctor.
Back pain accompanied by unexplained weight loss requires immediate medical attention.
Read:Lower Back Pain Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment
Here are 4 common underlying causes of back stiffness with or without pain:
1. Tight muscles in your thighs and hips
Our new album REASON is out now! Download/stream it at STAY IN TOUCH!Subscribe to Unspoken’s YouTube channel for o. Reason Code (2 byte) 2. Vendor Specific Information (one or more) 3. 802.11w (MFP) info. Here is a capture of a Deauthentication frame. In this case client station specify reason code as 3 – Deauthenticated because sending station is leaving BSS.Once AP receive this, it should send ACK to the client station.
Tightness in certain groups of muscles in your thighs and/or hips may alter the biomechanics of your spine. Common examples are:
Tight hamstrings
Your hamstring muscles run through the back of each of your thighs. These large and powerful group of muscles can become tight for a number of reasons, including physical inactivity or a lack of stretching before and/or after working out.
See Easy Hamstring Stretches
When your hamstrings are tight, they become shorter. These changes can affect the curvature of the lower part of your spine, disrupting the alignment of the spine with the pelvis (hip). As a result, you may feel stiffness in your lower back with or without pain. The stiffness is usually more pronounced when you bend your spine forward.1
Targeted hamstring stretching can gradually lengthen your hamstrings and relieve lower back stiffness.
Tight hip flexors
The iliopsoas muscle in your hip allows you to lift your thigh and bring it close to your body. This action is called flexion of the hip.
Tightness in the iliopsoas muscle can create stiffness within the segments of your spine. In severe iliopsoas tightness, spinal instability may occur. It is also possible for the surrounding spinal tissues to get inflamed and irritated, generating pain.2
See Back Muscles and Low Back Pain
Pressure on the spine can be relieved by stretches that help in lengthening the hip flexors.
2. Sitting with your spine curved forward
When you sit for a long time, the following changes occur in your spine:
- Increased pressure within each spinal segment3
- Reduced strength in the muscles of your upper and lower back3,4
- Decreased nutrient supply to the spinal tissues3
When you sit on the edge of your chair or hunch towards your computer, the strain on your spine is more—and can cause stiffness and pain.
See Identifying Incorrect Posture
A sedentary lifestyle can exacerbate these changes, causing spinal stiffness to develop within an hour of sitting.4
To avoid back stiffness, use an upright sitting posture. Roll your shoulders back with the ears over the shoulders and the upper arms parallel to your torso. While sitting in an office chair try to avoid constant use of the backrest and sit upright to activate your core muscles.
Reason 413
See Posture to Straighten Your Back
3. Inflammatory changes in your spine
Inflammation can cause the joints in your spine to become less flexible and/or fuse, resulting in stiffness. Two common examples are:
Ankylosing spondylitis
When spinal inflammation results in the gradual fusion between adjacent vertebrae, it is called ankylosing spondylitis. The condition causes progressive stiffness and chronic pain in the upper and/or lower back.5
The stiffness usually improves with exercise and does not improve with rest.5
Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis is the breakdown of the protective cartilage between the facet joints at the back of your spine. As a result, your joints create more friction upon movement, causing pain and stiffness.
The stiffness is usually present in the morning, tends to ease with movements during the day, and peaks again after long periods of inactivity or rest.
Both ankylosing spondylitis and spinal osteoarthritis can be treated with medication, exercise, and lifestyle changes.
4. Dehydration and shrinkage of your spinal discs
Your spinal discs are shock-absorbing pads between your vertebrae that distribute loads within your spine. Age-related changes can cause degeneration in these discs, altering their biomechanics.6
When a disc degenerates, there is a breakdown in its fibrocartilage component, loss of water, and a decrease in its height. These changes can cause spinal stiffness, especially during bending movements.7
See Lumbar Degenerative Disc Disease (DDD)
Treatment usually includes physical therapy, exercise, medications, and losing weight (if applicable). Rarely, surgery may be recommended.
See Lumbar Degenerative Disc Disease Treatment
If you experience back stiffness that does not resolve with self-care and/or affects your daily activities, talk to your doctor. A doctor can help identify the cause of your back stiffness and formulate a treatment plan for the underlying condition.
Learn more:
References
- 1.Jandre Reis FJ, Macedo AR. Influence of Hamstring Tightness in Pelvic, Lumbar and Trunk Range of Motion in Low Back Pain and Asymptomatic Volunteers during Forward Bending. Asian Spine J. 2015;9(4):535–540. doi:10.4184/asj.2015.9.4.535
- 2.Avrahami D, Potvin JR. The clinical and biomechanical effects of fascial-muscular lengthening therapy on tight hip flexor patients with and without low back pain. J Can Chiropr Assoc. 2014;58(4):444–455.
- 3.Gupta N, Christiansen CS, Hallman DM, Korshøj M, Carneiro IG, Holtermann A. Is objectively measured sitting time associated with low back pain? A cross-sectional investigation in the NOMAD study. PLoS One. 2015;10(3):e0121159. Published 2015 Mar 25. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0121159
- 4.Heneghan NR, Baker G, Thomas K, Falla D, Rushton A. What is the effect of prolonged sitting and physical activity on thoracic spine mobility? An observational study of young adults in a UK university setting. BMJ Open. 2018;8(5):e019371. Published 2018 May 5. doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2017-019371
- 5.Wenker KJ, Quint JM. Ankylosing Spondylitis. [Updated 2018 Nov 14]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2019 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK470173/
- 6.Newell N, Little J, Christou A, Adams M, Adam C, Masouros S. Biomechanics of the human intervertebral disc: A review of testing techniques and results. Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials. 2017;69:420-434. doi:10.1016/j.jmbbm.2017.01.037
- 7.Zirbel SA, Stolworthy DK, Howell LL, Bowden AE. Intervertebral disc degeneration alters lumbar spine segmental stiffness in all modes of loading under a compressive follower load. The Spine Journal. 2013;13(9):1134-1147. doi:10.1016/j.spinee.2013.02.010
This article helps you understand the most common settings that are used to establish a Remote Desktop session in an enterprise environment, and provides troubleshooting information for Remote desktop disconnected errors.
Applies to: Windows Server 2012 R2
Original KB number: 2477176
Note
This article is intended for use by support agents and IT professionals.
Remote Desktop Server
A Remote Desktop Session Host server is the server that hosts Windows-based programs or the full Windows desktop for Remote Desktop Services clients. Users can connect to an RD Session Host server to run programs, to save files, and to use network resources on that server. Users can access an RD Session Host server from within a corporate network or from the Internet.
Remote Desktop Session Host (RD Session Host) was formerly known as the Remote Desktop server role service, and Remote Desktop Session Host (RD Session Host) server was formerly known as Remote Desktop server.
Remote connections for administration
Remote Desktop supports two concurrent remote connections to the computer. You do not have to have Remote Desktop Services client access licenses (RDS CALs) for these connections.
To allow more than two administrative connections or multiple user connections, you must install the RD Session Host Role and have appropriate RDS CALs.
Symptom 1: Limited Remote Desktop session or Remote Desktop Services session connections
When you try to make a Remote Desktop Connection (RDC) to a remote computer or to a Remote Desktop server (Terminal Server) that is running Windows Server 2008 R2, you receive one of the following error messages:
Remote Desktop Disconnected.
This computer can't connect to the remote computer.
Try connecting again. If the problem continues, contact the owner of the remote computer or your network administrator.
Also, you are limited in the number of users who can connect simultaneously to a Remote Desktop session or Remote Desktop Services session. A limited number of RDP connections can be caused by misconfigured Group Policy or RDP-TCP properties in Remote Desktop Services Configuration. By default, the connection is configured to allow an unlimited number of sessions to connect to the server.
Symptom 2: Port assignment conflict
You experience a port assignment conflict. This problem might indicate that another application on the Remote Desktop server is using the same TCP port as the Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP). The default port assigned to RDP is 3389.
Symptom 3: Incorrectly configured authentication and encryption settings
After a Remote Desktop server client loses the connection to a Remote Desktop server, you experience one of the following symptoms:
- You cannot make a connection by using RDP.
- The session on the Remote Desktop server does not transition to a disconnected state. Instead, it remains active even though the client is physically disconnected from the Remote Desktop server.
If the client logs back in to the same Remote Desktop server, a new session may be established, and the original session may remain active.

Also, you receive one of the following error messages:
Error message 1
Because of a security error, the client could not connect to the Terminal server. After making sure that you are logged on to the network, try connecting to the server again.
Error message 2
Remote desktop disconnected. Because of a security error, the client could not connect to the remote computer. Verify that you are logged onto the network and then try connecting again.
Symptom 4: License certificate corruption
Remote Desktop Services clients are repeatedly denied access to the Remote Desktop server. If you are using a Remote Desktop Services client to log on to the Remote Desktop server, you may receive one of the following error messages.
Error message 1
Because of a security error, the client could not connect to the Terminal server. After making sure that you are logged on to the network, try connecting to the server again.
Error message 2
Remote desktop disconnected. Because of a security error, the client could not connect to the remote computer. Verify that you are logged onto the network and then try connecting again.
Error message 3
Because of a security error, the client could not connect to the Terminal server. After making sure that you are logged on to the network, try connecting to the server again.
Remote desktop disconnected. Because of a security error, the client could not connect to the remote computer. Verify that you are logged onto the network and then try connecting again.
Additionally, the following event ID messages may be logged in Event Viewer on the Remote Desktop server.
Event message 1
Event message 2
Event message 3
Event message 4
Event message 5
Resolution for Symptom 1
To resolve this problem, use the following methods, as appropriate.
Verify Remote Desktop is enabled
Open the System item in Control Panel. To start the System tool, click Start, click Control Panel, click System, and then click OK.
Under Control Panel Home, click Remote settings.
Click the Remote tab.
Under Remote Desktop, select either of the available options, depending on your security requirements:
Allow connections from computers from computers running any version of Remote Desktop (less secure)
Allow connections from computers only from computers running Remote Desktop with Network Level Authentication (more secure)
If you select Don't allow connections to this computer on the Remote tab, no users will be able to connect remotely to this computer, even if they are members of the Remote Desktop Users group.
Verify Remote Desktop Services Limit number of connections policy
Start the Group Policy snap-in, and then open the Local Security Policy or the appropriate Group Policy.
Locate the following command:
Local Computer Policy > Computer Configuration > Administrative Templates > Windows Components > Remote Desktop Services > Remote Desktop Session Host > Connections Limit number of connections
Click Enabled.
In the RD Maximum Connections allowed box, type the maximum number of connections that you want to allow, and then click OK.
Verify Remote Desktop Services RDP-TCP properties
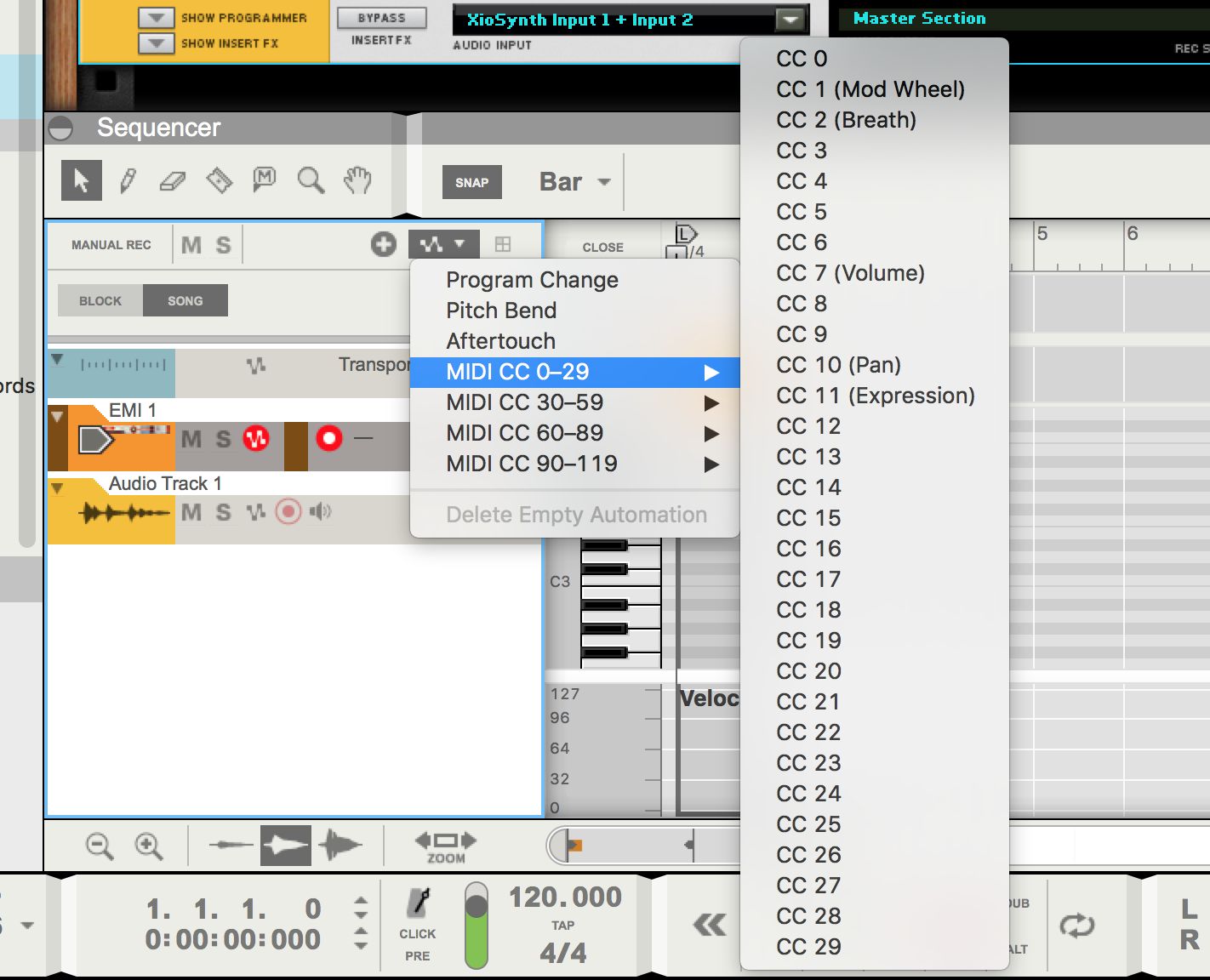
Follow these steps, depending on your operating system version.
Setting via Remote Desktop Services Configuration
Configure the number of simultaneous remote connections allowed for a connection:
On the RD Session Host server, open Remote Desktop Session Host Configuration. To open Remote Desktop Session Host Configuration, click Start, point to Administrative Tools, point to Remote Desktop Services.
Under Connections, right-click the name of the connection, and then click Properties.
On the Network Adapter tab, click Maximum connections, enter the number of simultaneous remote connections that you want to allow for the connection, and then click OK.
If the Maximum connections option is selected and dimmed, the Limit number of connections Group Policy setting has been enabled and has been applied to the RD Session Host server.
Verify Remote Desktop Services Logon rights
Configure the Remote Desktop Users Group.
The Remote Desktop Users group on an RD Session Host server grants users and groups permission to remotely connect to an RD Session Host server. You can add users and groups to the Remote Desktop Users group by using the following tools:
- Local Users and Groups snap-in
- The Remote tab in the System Properties dialog box on an RD Session Host server
- Active Directory Users and Computers snap-in, if the RD Session Host server is installed on a domain controller
You can use the following procedure to add users and groups to the Remote Desktop Users group by using the Remote tab in the System Properties dialog box on an RD Session Host server.
Membership in the local Administrators group, or equivalent, on the RD Session Host server that you plan to configure, is the minimum required to complete this procedure.
Add users and groups to the Remote Desktop Users group by using the Remote tab
Start the System tool. To do this, click Start, click Control Panel, click the System icon, and then click OK.
Under Control Panel Home, click Remote settings.
On the Remote tab in the System Properties dialog box, click Select Users. Add the users or groups that have to connect to the RD Session Host server by using Remote Desktop.
Note
If you select the Don't allow connections to this computer option on the Remote tab, no users will be able to connect remotely to this computer, even if they are members of the Remote Desktop Users group.
Add users and groups to the Remote Desktop Users group by using Local Users and Groups snap-in
- Click Start, click Administrative Tools, and then click Computer Management.
- In the console tree, click the Local Users and Groups node.
- In the details pane, double-click the Groups folder.
- Double-click Remote Desktop Users, and then click Add.
- In the Select Users dialog box, click Locations to specify the search location.
- Click Object Types to specify the types of objects that you want to search for.
- In the Enter the object names to select (examples) box, type the name you want to add.
- Click Check Names.
- When the name is located, click OK.
Note
- You can't connect to a computer that's asleep or hibernating, so make sure the settings for sleep and hibernation on the remote computer are set to Never. (Hibernation isn't available on all computers.) For information about making those changes, see Change, create, or delete a power plan (scheme).
- You can't use Remote Desktop Connection to connect to a computer using Windows 7 Starter, Windows 7 Home Basic, or Windows 7 Home Premium.
- Members of the local Administrators group can connect even if they are not listed.
Resolution for Symptom 2
Important
This section, method, or task contains steps that tell you how to modify the registry. However, serious problems might occur if you modify the registry incorrectly. Therefore, make sure that you follow these steps carefully. For added protection, back up the registry before you modify it. Then, you can restore the registry if a problem occurs. For more information about how to back up and restore the registry, seeHow to back up and restore the registry in Windows.
To resolve this problem, determine which application is using the same port as RDP. If the port assignment for that application cannot be changed, change the port assigned to RDP by changing the registry. After you change the registry, you must restart the Remote Desktop Services service. After you restart the Remote Desktop Services service, you should verify that the RDP port has been changed correctly.
Remote Desktop server listener availability
The listener component runs on the Remote Desktop server and is responsible for listening for and accepting new Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) client connections, thereby allowing users to establish new remote sessions on the Remote Desktop server. There is a listener for each Remote Desktop Services connection that exists on the Remote Desktop server. Connections can be created and configured by using the Remote Desktop Services Configuration tool.
To perform these tasks, refer to the following sections.
Determine which application is using the same port as RDP
You can run the netstat tool to determine whether port 3389 (or the assigned RDP port) is being used by another application on the Remote Desktop server:
- On the Remote Desktop server, click Start, click Run, type cmd, and then click OK.
- At the command prompt, type
netstat -a -oand then press Enter. - Look for an entry for TCP port 3389 (or the assigned RDP port) with a status of Listening. This indicates another application is using this port. The PID (Process Identifier) of the process or service using that port appears under the PID column.
To determine which application is using port 3389 (or the assigned RDP port), use the tasklist command-line tool along with the PID information from the netstat tool:
- On the Remote Desktop server, click Start, click Run, type cmd, and then click OK.
- Type
tasklist /svcand then press Enter. - Look for an entry for the PID number that is associated with the port (from the netstat output). The services or processes that are associated with that PID appear on the right.
Change the port assigned to RDP
You should determine whether this application can use a different port. If you cannot change the application's port, you must change the port that is assigned to RDP.
Important
We recommend that you do not change the port that is assigned to RDP.
If you have to change the port assigned to RDP, you must change the registry. To do this, you must be a member of the local Administrators group, or you must have been granted the appropriate permissions.
To change the port that is assigned to RDP, follow these steps:
On the Remote Desktop server, open Registry Editor. To open Registry Editor, click Start, click Run, type regedit, and then click OK.
If the User Account Control dialog box appears, verify that the action it displays is what you want, and then click Continue.
Locate and then click the following registry subkey:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESYSTEMCurrentControlSetControlRemote Desktop serverWinStations
RDP-TCP is the default connection name. To change the port for a specific connection on the Remote Desktop server, select the connection under the WinStations key:
- In the details pane, double-click the PortNumber registry entry.
- Type the port number that you want to assign to RDP.
- Click OK to save the change, and then close Registry Editor.
Restart the Remote Desktop Services service
For the RDP port assignment change to take effect, stop and start the Remote Desktop Services service. To do this, you must be a member of the local Administrators group, or you must have been granted the appropriate permissions.
Denial Reason 4
To stop and start the Remote Desktop Services service, follow these steps:
On the Remote Desktop server, open the Services snap-in. To do this, click Start, point to Administrative Tools, and then click Services.
If the User Account Control dialog box appears, verify that the action it displays is what you want, and then click Continue.
In the Services pane, right-click Remote Desktop Services, and then click Restart.
If you are prompted to restart other services, click Yes.
Verify that the Status column for the Remote Desktop Services service displays a Started status.
Verify that the RDP port has changed
To verify that the RDP port assignment has been changed, use the netstat tool:
On the Remote Desktop server, click Start, click Run, type cmd, and then click OK.
At the command prompt, type
netstat -athen press Enter.Look for an entry for the port number that you assigned to RDP. The port should appear in the list and have a status of Listening.
Important
Remote Desktop Connection and the Terminal server Web Client use port 3389, by default, to connect to a Remote Desktop server. If you change the RDP port on the Remote Desktop server, you will have to modify the port used by Remote Desktop Connection and the Remote Desktop server Web Client. For more information, see Change the listening port for Remote Desktop on your computer.
Verify that the listener on the Remote Desktop server is working
To verify that the listener on the Remote Desktop server is working correctly, use any of the following methods.
Note
RDP-TCP is the default connection name and 3389 is the default RDP port. Use the connection name and port number specific to your Remote Desktop server configuration.
Method 1
Use an RDP client, such as Remote Desktop Connection, to establish a remote connection to the Remote Desktop server.
Method 2
Use the qwinsta tool to view the listener status on the Remote Desktop server:
- On the Remote Desktop server, click Start, click Run, type cmd, and then click OK.
- At the command prompt, type qwinsta, and then press Enter.
- The RDP-TCP session state should be Listen.
Method 3
Use the netstat tool to view the listener status on the Remote Desktop server:
- On the Remote Desktop server, click Start, click Run, type cmd, and then click OK.
- At the command prompt, type
netstat -athen press Enter. - The entry for TCP port 3389 should be Listening.
Method 4
Use the telnet tool to connect to the RDP port on the Remote Desktop server:
- From another computer, click Start, click Run, type cmd, and then click OK.
- At the command prompt, type
telnet <servername> 3389, where <servername> is the name of the Remote Desktop server, and then press Enter.
If telnet is successful, you receive the telnet screen and a cursor.
If telnet is not successful, you receive the following error message:
Connecting To servername... Could not open connection to the host, on port 3389: Connect failed
The qwinsta, netstat, and telnet tools are also included in Windows XP and Windows Server 2003. You can also download and use other troubleshooting tools, such as Portqry.
Resolution for Symptom 3
To resolve the issue, configure authentication and encryption.
To configure authentication and encryption for a connection, follow these steps:
On the RD Session Host server, open Remote Desktop Session Host Configuration. To open Remote Desktop Session Host Configuration, click Start, point to Administrative Tools, point to Remote Desktop Services, and then click Remote Desktop Session Host Configuration.
Under Connections, right-click the name of the connection, and then click Properties.
In the Properties dialog box for the connection, on the General tab, in Security layer, select a security method.
In Encryption level, click the level that you want. You can select Low, Client Compatible, High, or FIPS Compliant. See Step 4 above for Windows Server 2003 for Security layer and Encryption level options.
Note
- To perform this procedure, you must be a member of the Administrators group on the local computer, or you must have been delegated the appropriate authority. If the computer is joined to a domain, members of the Domain Admins group might be able to perform this procedure. As a security best practice, consider using Run as to perform this procedure.
- To open Remote Desktop Services Configuration, click Start, click Control Panel, double-click Administrative Tools, and then double-click Remote Desktop Services Configuration.
- Any encryption level settings that you configure in Group Policy override the configuration that you set by using the Remote Desktop Services Configuration tool. Also, if you enable the System cryptography: Use FIPS compliant algorithms for encryption, hashing, and signing Group Policy setting, this setting overrides the Set client connection encryption level Group Policy setting.
- When you change the encryption level, the new encryption level takes effect the next time a user logs on. If you require multiple levels of encryption on one server, install multiple network adapters and configure each adapter separately.
- To verify that certificate has a corresponding private key, in Remote Desktop Services Configuration, right-click the connection for which you want to view the certificate, click the General tab, click Edit, click the certificate that you want to view, and then click View Certificate. At the bottom of the General tab, the statement, You have a private key that corresponds to this certificate, should appear. You can also view this information by using the Certificates snap-in.
- The FIPS compliant setting (the System cryptography: Use FIPS compliant algorithms for encryption, hashing, and signing setting in Group Policy or the FIPS Compliant setting in Remote Desktop server Configuration) encrypts and decrypts data sent from the client to the server and from the server to the client, with the Federal Information Processing Standard (FIPS) 140-1 encryption algorithms, using Microsoft cryptographic modules. For more information, see Terminal Services in Windows Server 2003 Technical Reference.
- The High setting encrypts data sent from the client to the server and from the server to the client by using strong 128-bit encryption.
- The Client Compatible setting encrypts data sent between the client and the server at the maximum key strength supported by the client.
- The Low setting encrypts data sent from the client to the server using 56-bit encryption.
Additional troubleshooting step: Enable CAPI2 event logs
To help troubleshoot this problem, enable CAPI2 event logs on both the client and server computers. This command is shown in the following screenshot.
Workaround for the issue (You cannot completely disconnect a Remote Desktop server connection) described in Symptom 3
To work around this problem, follow these steps:
- Click Start, click Run, type gpedit.msc, and then click OK.
- Expand Computer Configuration, expand Administrative Templates, expand Windows Components, expand Remote Desktop Services, expand Remote Desktop Session Host, and then click Connections.
- In the right pane, double-click Configure keep-alive connection interval.
- Click Enabled, and then click OK.
- Close Group Policy Object Editor, click OK, and then quit Active Directory Users and Computers.
Resolution for Symptom 4
Important
This section, method, or task contains steps that tell you how to modify the registry. However, serious problems might occur if you modify the registry incorrectly. Therefore, make sure that you follow these steps carefully. For added protection, back up the registry before you modify it. Then, you can restore the registry if a problem occurs. For more information about how to back up and restore the registry, see 322756 How to back up and restore the registry in Windows.
To resolve this problem, back up and then remove the X509 Certificate registry keys, restart the computer, and then reactivate the Remote Desktop Services Licensing server. To do this, follow these steps.
Reason 400 Error
Note
Perform the following procedure on each of the Remote Desktop servers.
Make sure that the Remote Desktop server registry has been successfully backed up.
Start Registry Editor.
Locate and then click the following registry subkey:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESYSTEMCurrentControlSetControlTerminal ServerRCMOn the Registry menu, click Export Registry File.
Type exported- Certificate in the File name box, and then click *Save.
Note
If you have to restore this registry subkey in the future, double-click the Exported-parameters.reg file that you saved in this step.
Right-click each of the following values, click Delete, and then click Yes to verify the deletion:
- Certificate
- X509 Certificate
- X509 Certificate ID
- X509 Certificate2
Exit Registry Editor, and then restart the server.
Reason 4 License Number
References
For more information about Remote Desktop Gateway, see the following articles:
Reason 4 Life
If this article does not help you resolve the problem, or if you experience symptoms that differ from those that are described in this article, visit the Microsoft Support for more information. To search your issue, in the Search support for help box, type the text of the error message that you received, or type a description of the problem.