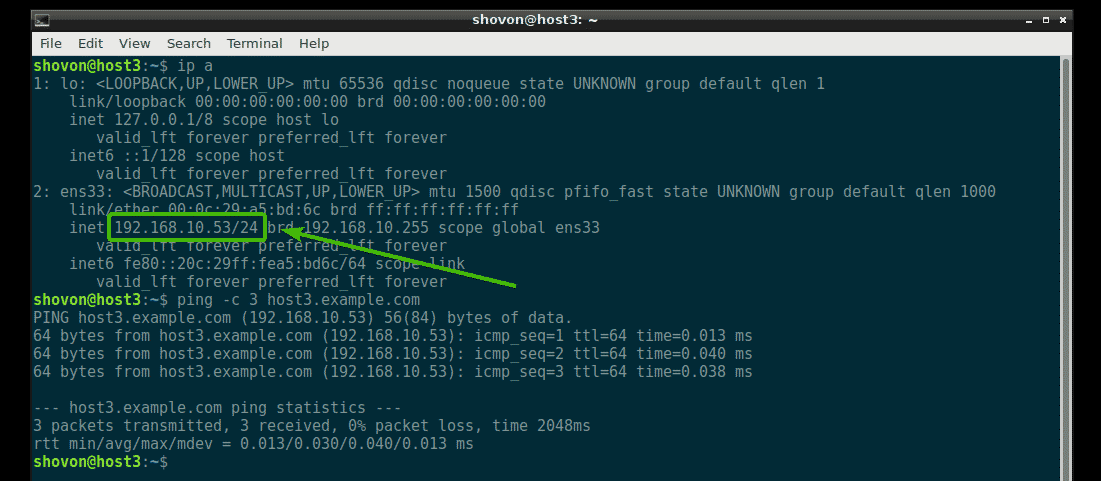
I just installed Ubuntu 18.04, and after i configured my web server i wanted to also replace the base dnsmasq since i needed support for wildcards. After I installed dnsmasq using this quide, the. Next, you will need to configure a remote client to use your Dnsmasq DNS server as the default DNS server. First, install DNS tools with the following command: apt-get install dnsutils ldnsutils -y. Once installed, you will need to edit the /etc/resolv.conf file and your Dnsmasq DNS server entry. Nano /etc/resolv.conf. Create a DHCP and DNS Server with Dnsmasq on Ubuntu Server 18.04 Published 18th Dec 2019. This tutorial will show you how to install and configure Dnsmasq on Ubuntu Server 18.04 so that DNS requests by clients on your network are cached.
In Ubuntu Bionic, I found that the dnsmasq package no longer creates a service for dnsmasq that you can control with service or systemctl. After a fair amount of experimenting and some help from the friendly folk at #systemd on irc.freenode.net , I ended up with a dnsmasq service file that does the right things, namely:
- wait for the LAN interface to be online (since my dnsmasq listens only on LAN), and then start the dnsmasq service.

Here goes the systemd unit file which you can place in /etc/systemd/system/dnsmasq.service :
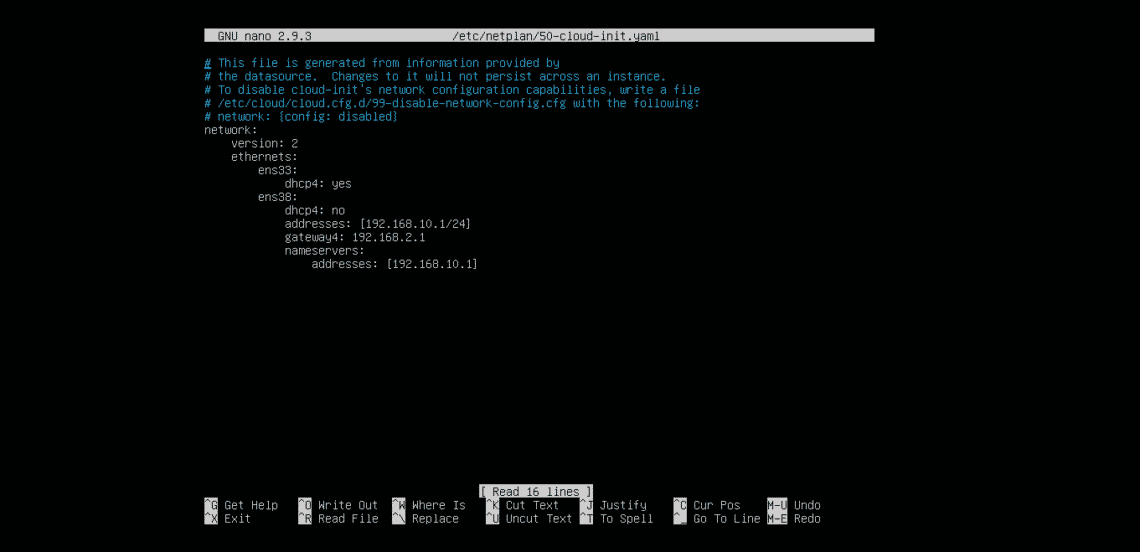
Once you have created the service file, you must enable it with sudo systemctl enable dnsmasq.service . You of course need to make sure to use the correct device names for your system (my network device is listed by systemctl as sys-subsystem-net-devices-enp4s0.device). You can list all the devices systemd knows on your machine using systemctl -t device. Use grep to filter for your specific device (interface) name if you know what it’s called. Mine was called “enp4s0”.

Ubuntu 18.04 Disable Dnsmasq
The short summary of the above systemd unit file is that:
Remove Dnsmasq Ubuntu 18.04
- It is wanted by my LAN ethernet device, so it is launched when the device has been registered by udevd (or whatever subsystem handles this).
- It’s of type “forking” because dnsmasq is a daemon which forks itself and you need this configuration for systemd to track it correctly.
- In order to wait until the LAN is actually routable, I had to use the
ExecStartPre(thanks #systemd) to use the systemd-networkd-wait-online application.- ExecStartPre just executes specified binary or script before it actually launches your desired process.
- this application basically blocks until the specified interface is routable (which means it has an IP address).
- You must use the full path to the executable.
- Once it’s routable, then dnsmasq is executed (ExecStart), and dnsmasq by default will load the config file in /etc/dnsmasq.conf